NAUI
Open Water SCUBA Comprehensive Exam
Section
I – NAUI
1.) Define two of the following types of diving:
a. Skin Diving
b. Recreation/Sport SCUBA Diving
c. Commercial Diving
d. Technical Diving
2.) After completing a NAUI Open Water course you are certified to dive: _________________________________________________________________
3.) What is the ultimate risk in SCUBA?
4.) List two medical conditions or lifestyles that would prevent a person from diving and explain why.
a.
b.
5.) Which is the most common cause of diving accidents: Human Error or Equipment Malfunction
Section
II – Diving Equipment
1.) _________ is the most important aspect when selecting SCUBA Equipment
2.) What are the two materials from which SCUBA Cylinders are made?
3.) _________ testing is the only test federally required.
4.) List Skin Diving Gear:
5.) List SCUBA Diving Gear.
6.) What type of glass is used for masks and why?
7.) What’s the difference between a J & K Valve?
8.) What do these markings mean:
a.
3
b. 3 AA 2400: __________
c. P548067: __________
d. 5 Δ 03: __________
9.) _________ occur when fins that are too large and/or stiff are used.
10.) List several types of Alternate Air Sources
11.) What is the most crucial thing to remember when rinsing your regulator?
12.) Tell me everything you know about regulators. Key words to use: 1st stage, 2nd stage, Intermediate Pressure, Ambient Pressure, low pressure power inflator, SPG and high pressure port
Section
III – Diving Physics
1.) True or False – Air is a gas
2.) Identify these percentages
a. 78.084%
b. 20.946%
c. .934%
d. .003%
3.)
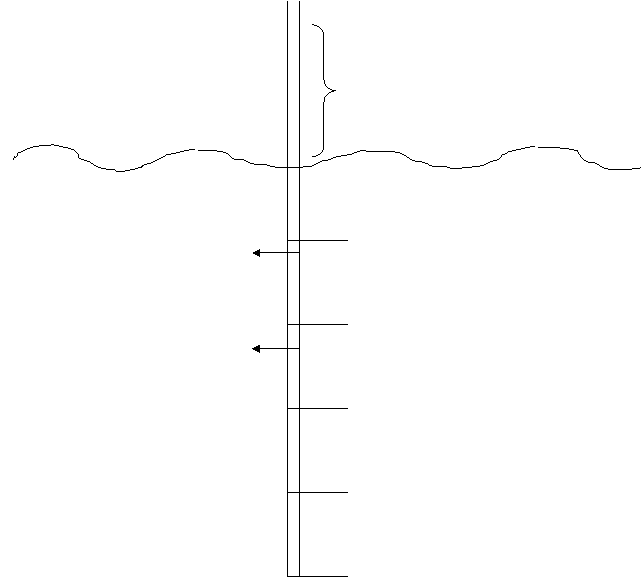 Fill in the blanks:
Fill in the blanks:
= _____ ATA = _______ p.s.i.
Fresh Water Salt Water
33 fsw = _____ atm = _____ ATA
_____ ATA = _____ ffw
fsw = _____ ATA
_____ ATA = _____ ffw
fsw = _____ ATA
fsw = _____ ATA
fsw = _____ ATA
4.) In what order are colors absorbed?
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
5.) Sound travels __________ in water than in air.
6.) Light travels __________ in water than in air which makes objects appear __________ and __________.
7.) As the Total Pressure exerted by a mixture of gases increases, the partial pressure exerted by a gas __________.
8.) As Pressure increases, Volume __________.
9.) As Pressure increases, Temperature __________.
10.) Heat is absorbed __________ times faster in water than in air making it necessary to wear an __________ when diving in cooler water.
11.) At 33 fsw the pressure doubles which means that the total pressure exerted by a gas mixture also doubles. If the partial pressure of Oxygen at the surface is .21, what will the partial pressure be at 33 fsw?
12.) A sealed balloon filled with air that has a volume of 6 cubic inches at 132 fsw will have what volume at 33 fsw?
P1
= 5 ATA
P1V1 = P2V2
V1
= 6 cu in
( 5 ATA) ( 6 cu in) = ( 2 ATA) ( X cu in)
P1
= 2 ATA
_____ = _____X
V1 = X X = _____ cu in
13.) A sealed balloon filled with air that has a volume of 4 cu in at 99 fsw will have what volume at the surface?
P1
= 4 ATA
P1V1 = P2V2
V1
= 4 cu in
(_____ ATA) (_____ cu in) = (_____ ATA) (X cu in)
P2
= 1 ATA
_____ = _____ X
V2 = X cu in X = _____ cu in
14.) A sealed balloon with 1 cu ft of air at the surface will have how many cu ft of air at 33 fsw?
P1
= _____ ATA
P1V1 = P2V2
V1
= _____ cu ft
(_____ ATA) (_____ cu ft) = (_____ ATA) (X cu in)
P2
= _____ ATA
_____ = _____ X
V2 = X cu in X = _____ cu ft
15.) A sealed lift bag filled with 2 cu ft of air at 165 fsw will have how many cu ft of air at 66 fsw?
P1
= _____ ATA
V1
= _____ cu ft
P2
= _____ ATA
V2 = X cu in
16.) A .5 cu ft chest that weighs 128 lbs is sitting on the bottom of the ocean. How many 1 cu ft lift bags are needed to lift it to the surface?
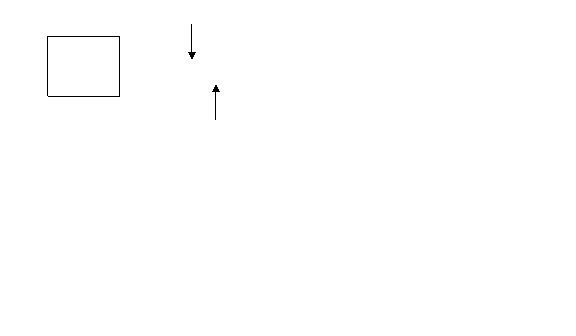
300 lbs 300 - _____ = X
.75 cu ft X / 64 = _____
_____ lift bags are needed
(.75) (64) = _____ lbs
17.) A 1 cu ft chest that weighs 200 lbs is sitting on the bottom of the ocean. How many 1 cu ft lift bags are needed to lift it to the surface?

_____ lbs _____ - _____ = X
1 cu ft X / _____ = _____
_____ lift bags are needed
(1) ( 64) = _____ lbs
Section
IV – Diving Physiology
1.) __________ is a protein in red blood cells that increases the Oxygen carrying ability of blood.
2.) The __________ are microscopic air sacks in the lungs where the exchange of gases takes place.
3.) Cells need this gas for metabolism. __________
4.) This gas is a waste product of human respiration. __________
5.) List 3 things that effect respiration:
a.
b.
c.
6.) List several air spaces in the human body:
a.
b.
c.
7.) Describe one method of clearing one’s ears:
8.) How do you equalize mask pressure?
9.) Why is diving with a cold not recommended?
10.) For each lung overpressure injury, please list the cause, symptoms, treatment and method of prevention:
I. Pneumothorax
a. Cause
b. Symptoms
c. Treatment
d. Prevention
II. Mediastinal Emphysema
a. Cause
b. Symptoms
c. Treatment
d. Prevention
III. Subcutaneous Emphysema
a. Cause
b. Symptoms
c. Treatment
d. Prevention
IV. Arterial Gas Embolism (AGE)
a. Cause
b. Symptoms
c. Treatment
d. Prevention
11.) Hyperventilation is not recommended for diving because of:
12.) Hypoventilation (__________ breathing) is not recommended because of __________ excess. Its symptoms include __________. What is inherently wrong with __________ breathing?
13.) Martini’s law refers to: __________
a. Cause
b. Symptoms
c. Prevention
14.) Decompression Sickness:
a. Cause
b. Symptoms
c. Treatment
d. Prevention
Section
V – Dive Tables
I. A diver dives to 65 fsw for 20 minutes.
a. Letter Group Designation:
He then has a surface interval of 2 hours.
b. New Letter Group Designation:
He plans to dive again to 50 fsw
c. Adjusted Maximum Dive Time:
d. Residual Nitrogen Time:
II. A diver dives to 82 fsw for 35 minutes then has a surface interval of 3 hrs. She plans to dive again to 70 fsw.
a. Letter Group Designation after Dive 1:
b. Letter Group after Surface Interval:
c. Adjusted Max Dive Time for 2nd Dive:
d. Residual Nitrogen Time:
III. Dive 1 – 100 fsw for 15 minutes. Surface Interval – 2 hrs.
a. Letter Group Designation after Surface Interval
Diver plans to dive again to 70 fsw
b. Adjusted Max Dive Time
c. Residual Nitrogen Time
Diver has an actual dive time of 20 minutes
d. Total Nitrogen Time
IV. Dive 1 – 70 fsw for 40 minutes. Surface Interval – 3 hrs 30 minutes
a. Letter Group Designation after Surface Interval:
Plans second dive to 70 fsw
b. Adjusted Maximum Dive Time:
c. Residual Nitrogen Time:
Actual dive time to 70 fsw was 15 minutes
d. Total Nitrogen Time:
e. Letter Group Designation:
She remains on the surface for 2 hrs
f. New Letter Group:
She plans to do a 3rd dive to 80 fsw
g. Residual Nitrogen Time:
What will her Total Nitrogen Time be if her Actual Dive Time is equal to her Adjusted Max Dive Time?
h. Total Nitrogen Time:
Multiple
Choice Section
1.) A diver with a group letter of “F” making a dive to 60 fsw has a residual nitrogen time of:
a. 47 minutes c. 19 minutes
b. 36 minutes d. 30 minutes
2.) It is advisable that a sport/recreational diver:
a. Make few decompression dives
b. Make decompression dives if he/she feels psychologically prepared.
c. Avoid decompression dives
d. Execute decompression dives when a hyperbaric chamber is nearby.
3.) For optimum no-decompression bottom times, plan repetitive dives so that each successive dive is to ______ depth.
a. a deeper c. a shallower
b. the same d. equal
4.) The maximum dive time for a dive to 60 fsw is ______ minutes.
a. no limit c. 60
b. 55 d. 100
5.) The minimum surface interval required to avoid stage decompression after a dive to 88 fsw for 18 minutes, followed by a dive to 78 fsw for 23 minutes is:
a. 46 minutes c. 2 hr, 29 minutes
b. 1 hr, 30 minutes d. 3 hr, 58 minutes
6.) According to NAUI, a repetitive dive is defined as more than one dive within a period of ______ hours.
a. 6 c. 18
b. 12 d. 24
7.) The minimum surface interval recommended between two dives is ______ minutes.
a. 30 c. 180
b. 60 d. 240
8.) Your first dive is to 60 fsw for 50 minutes. You spend one hour and 40 minutes on the surface, what is your adjusted maximum dive time at 60 fsw?
a. 36 minutes c. 60 minutes
b. 19 minutes d. 30 minutes
9.) A buddy team in a NAUI Master SCUBA Diver Course makes an ocean dive to 95 fsw for 20 minutes. After a surface interval of 2 hours and 35 minutes, they make a repetitive dive to 70 fsw for 24 minutes. They remain on the surface for 2 hours and 51 minutes before diving to 45 feet. What is their adjusted maximum dive time for the 3rd dive?
a. 29 minutes c. 42 minutes
b. 51 minutes d. 59 minutes
Section VI Dive Time Planning
1.) What things need to be considered in a site evaluation?
2.) What is the emergency procedure for a lost or separated buddy?
3.) When someone signals “OK” you should:
4.) Why is it important to review hand signals before entering the water?
5.) What does diving ‘activity’ refer to?
6.) When is an Emergency Swimming Ascent Recommended? When is an Emergency Buoyant Ascent Recommended?
What ‘wrong’ thing did the diver do in the demonstration for an Emergency Buoyant Ascent on the video?